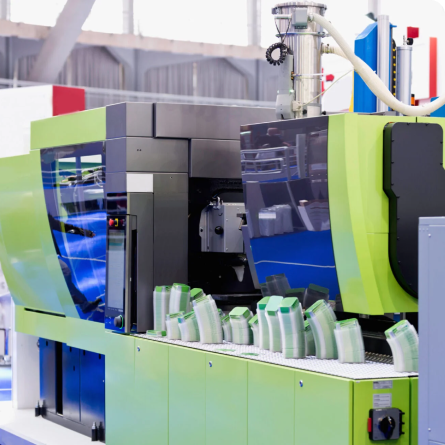
An injection molding machine is an industrial device used for shaping plastics by injecting them under pressure into a mold, where the material solidifies and then takes on the desired shape. These machines can be found in various types of factories and industrial facilities.

Injection molding machine components
Below are described the key components of an injection molding machine:
Material tank
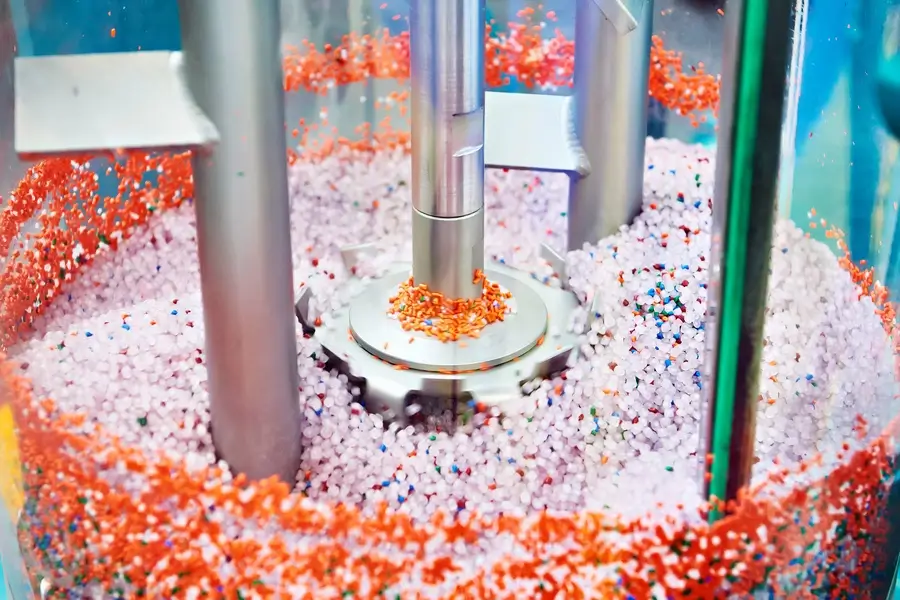
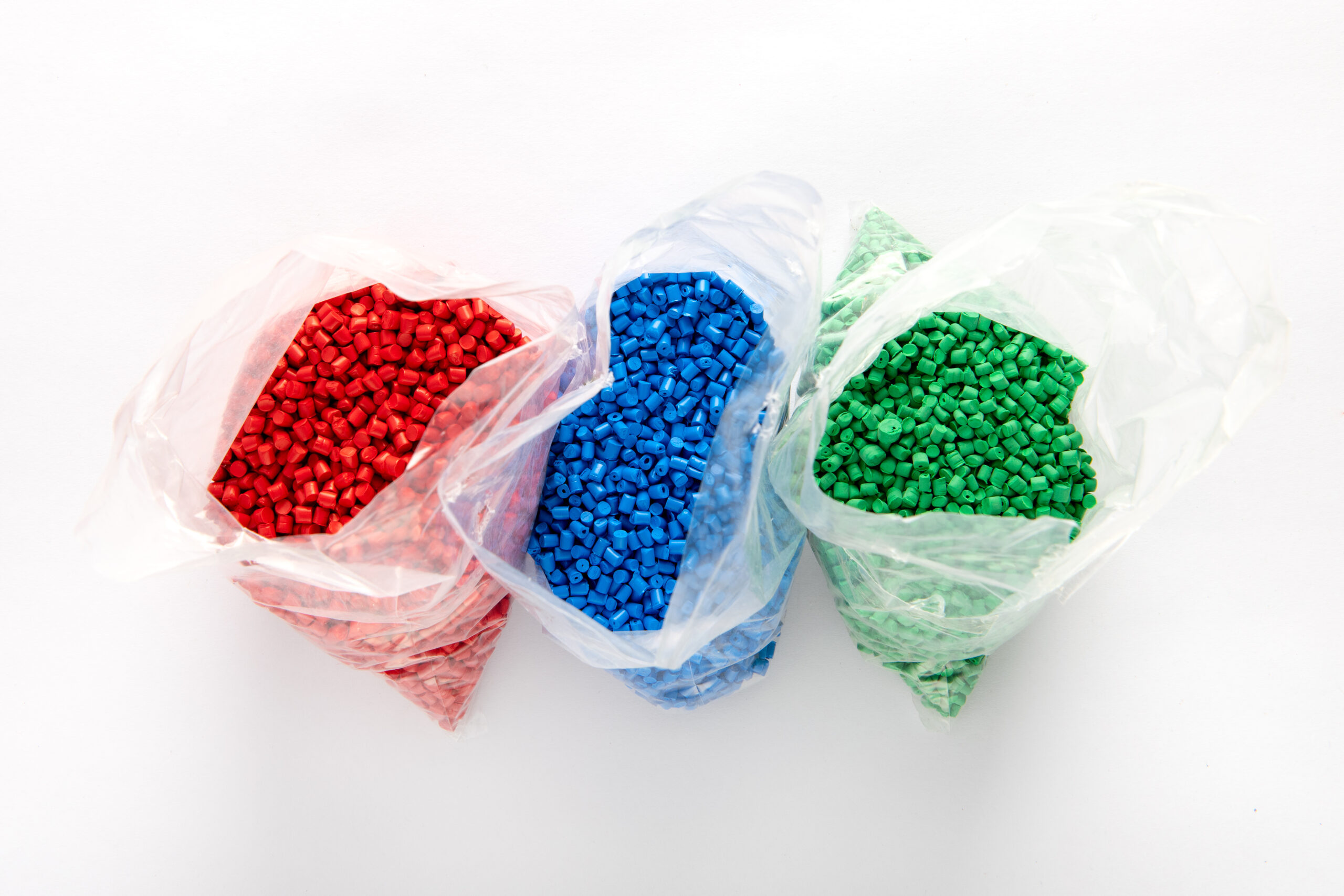
The injection molding machine has a material tank. It contains the material used in the process. Plastic material is in the form of small pellets, hence its industry name is “granulate”. An important aspect when using most materials is the proper pre-drying of the granulate. After being introduced into the tank, the raw material is transferred to the injection section.
Screw
The injection molding machine must have a screw, which is located in the injection section. It is a spiral that rotates and pushes the material forward. As the raw material is moved, it is mixed and gradually melted due to the heat generated.
Cylinder
The screw moves inside a cylinder, which is heated to melt the raw material. This is important because when the used material reaches the right temperature, it becomes pliable, and only in this form can it be molded. The cylinder has distinct zones of different temperatures, which aid in melting the material and maintaining the correct viscosity during injection. Temperature is controlled through a heating system.
Injection unit
At the end of the cylinder, there is an injection unit with an adjustable nozzle. When the material is sufficiently melted, it is then injected into the mold at very high pressure.
Nozzle
It is located at the end of the injection molding machine’s cylinder. Its main function is to control the flow of molten material from the cylinder into the mold while maintaining the appropriate parameters such as pressure and velocity.
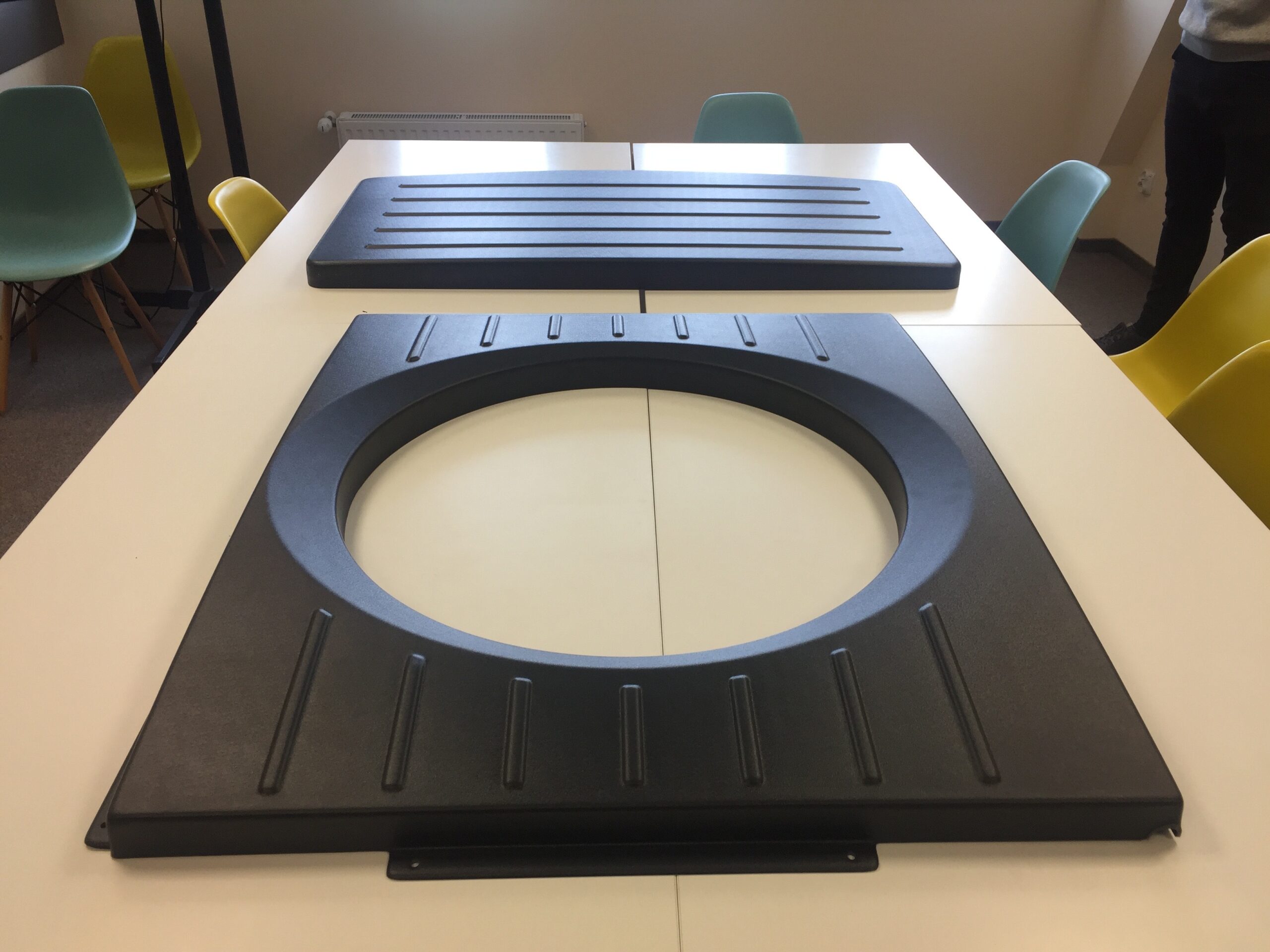
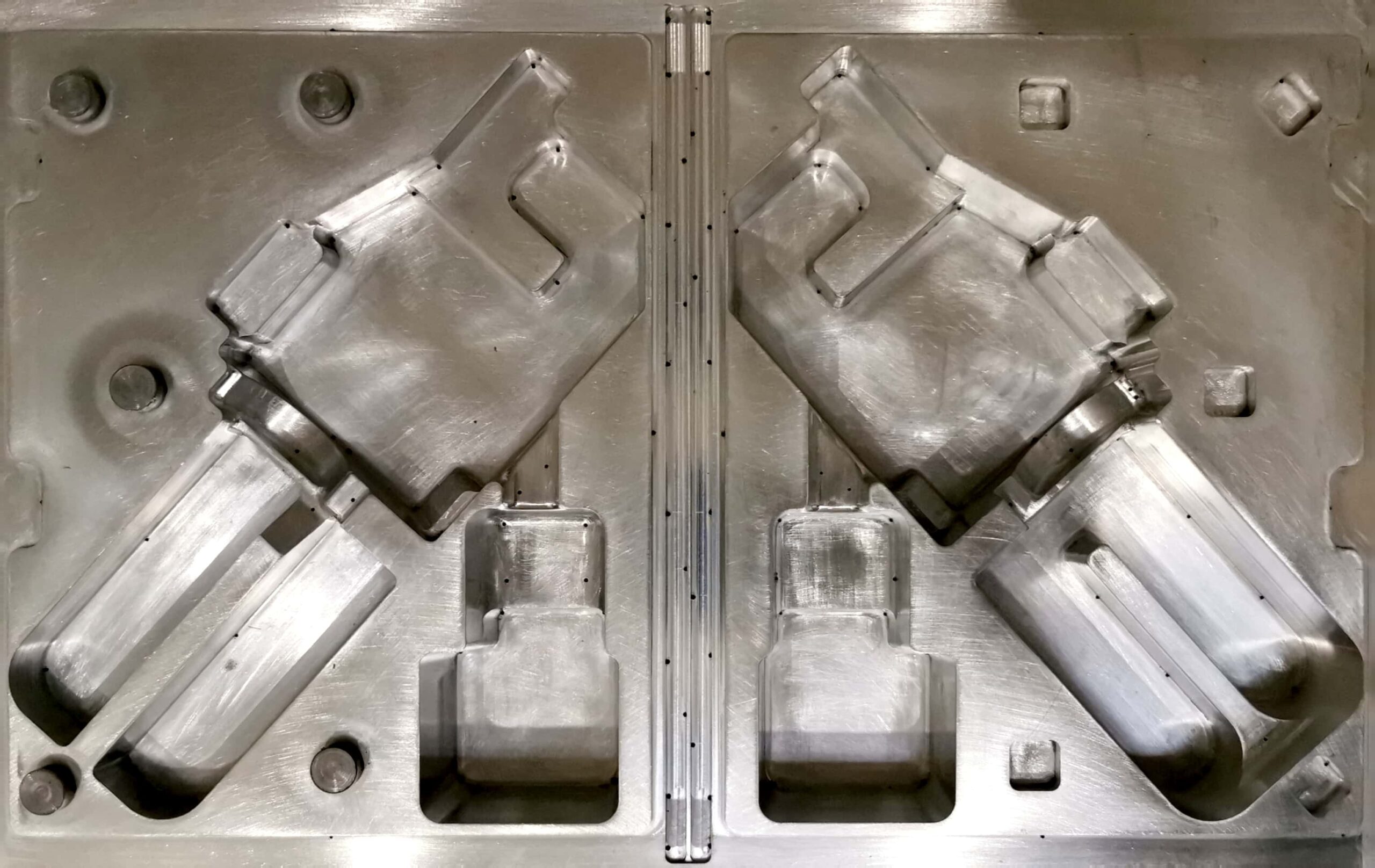
Mold
It is a tool whose internal shape corresponds to the shape of the product we want to manufacture. It is in the mold that, after injecting the plasticized material, it cools and solidifies, taking on the desired shape.
Don't wait!
Tailor the technology to your needs to reduce plastic production costs.
Injection molding systems
In the structure of an injection molding machine, one can also identify the following systems:
Cooling system
The mold is surrounded by a cooling system, which consists of pipes or channels through which a cooling fluid (most commonly water) flows. The molded part (the product of the injection process) needs to be cooled because it would be impossible to eject otherwise. Firstly, the material needs to solidify (it is introduced in a pliable, easily moldable state). A secondary aspect is the fact that the molded part is simply very hot (usually at temperatures around 100°C or more).
Mold opening and closing system
After the product has cooled and hardened, the mold is opened, and the finished product is removed. Once the molded part has been taken out, the mold is closed, and the cycle is repeated. The closing force is adjusted individually based on the product and the machine.
Control system
Injection molding machines are equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise control of the injection process. The operator can adjust parameters such as temperature, pressure, injection time, etc. Thanks to this, the process can be fully automated.
Hydraulic system
Many injection molding machines use hydraulic systems to generate the necessary pressure for screw drive and material injection. However, modern models on the market can also utilize electric drive systems.
How an injection molding machine works
The technology of plastic injection molding is becoming increasingly popular among customers due to its versatility and capabilities. What exactly does it involve?
Description of the process
The injection molding process begins with supplying the injection molding machine with raw material in the form of granules. The material is placed in the machine’s hopper, and then the screw starts to rotate, pushing the material forward in the cylinder.
As the material moves, the raw material granules are gradually heated and melted, forming a homogeneous, plasticized mass. Different temperature zones exist within the cylinder, allowing for gradual melting and blending of the material. Once the material is adequately melted, the screw moves forward, generating high pressure.
The injection unit, located at the end of the cylinder, injects the molten material into the mold at very high pressure. The mold has an internal shape corresponding to the desired product. After injecting the material into the mold, it begins to cool and solidify.
Inside the mold, there is a cooling system that allows for the cooling of the product. The duration of this stage depends on the type of material, the thickness of the product, and its geometry. After the product has cooled, the mold is opened, and the finished product is removed from the mold.
The injection molding process is cyclic, which means that after the finished product is removed, the mold is closed again, and the process begins anew. The entire cycle is automatically repeated, enabling mass production.

What are the key points to focus on?
In the injection molding process, it is crucial to precisely adjust parameters such as material temperature, injection pressure, cooling time, etc., according to the type of material and the desired product. Advanced injection molding control systems allow for precise control of these parameters, which significantly impacts the quality and properties of the final product.
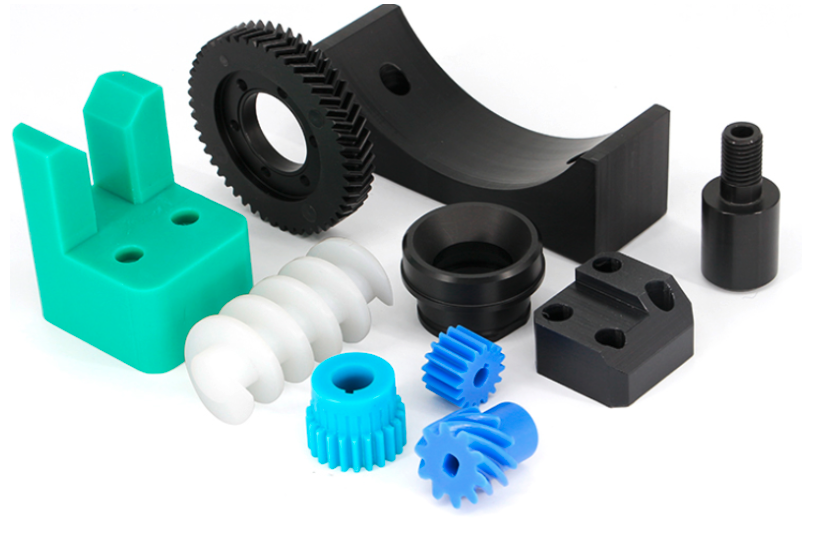
What plastic products can be manufactured using an injection molding machine?
The injection molding machine enables the production of a wide range of plastic components and products that find applications in various industries. In terms of plastic components, the following industries can be highlighted:
- Electrical/Electronic industry → These products must exhibit precision. These include enclosures, connectors, and protective covers, among others.
- Automotive → These components must be of the appropriate quality and have an aesthetic finish. These include engine covers and headlight housings, among others.
- Household articles → In this category, many plastic components can be distinguished, including door handles and combs, among others.
- Toys → ranging from small figures to more complex models.
- Medical articles → including items such as test tubes, measuring components, and specialized containers, among others.
- Aviation → in this industry, components must be lightweight and durable, making plastic elements an ideal choice. These include lighting fixtures, engine components, and avionics equipment, among others.
Summary
Injection molding machines are crucial tools in the industry, enabling precise production of various plastic materials. The injection molding process involves melting the raw material, injecting it under pressure into a mold, and obtaining products of the desired quality. Injected plastic products provide lightweight and durable components that meet rigorous standards. With technological advancements, injection molding machines focus on innovations such as biodegradable materials and more efficient recycling processes. These tools continue to shape the industry, creating a wide range of products, from everyday items to advanced components.
Are you considering production using an injection molding machine? Consult your project with us, and our engineers will analyze the technological possibilities.