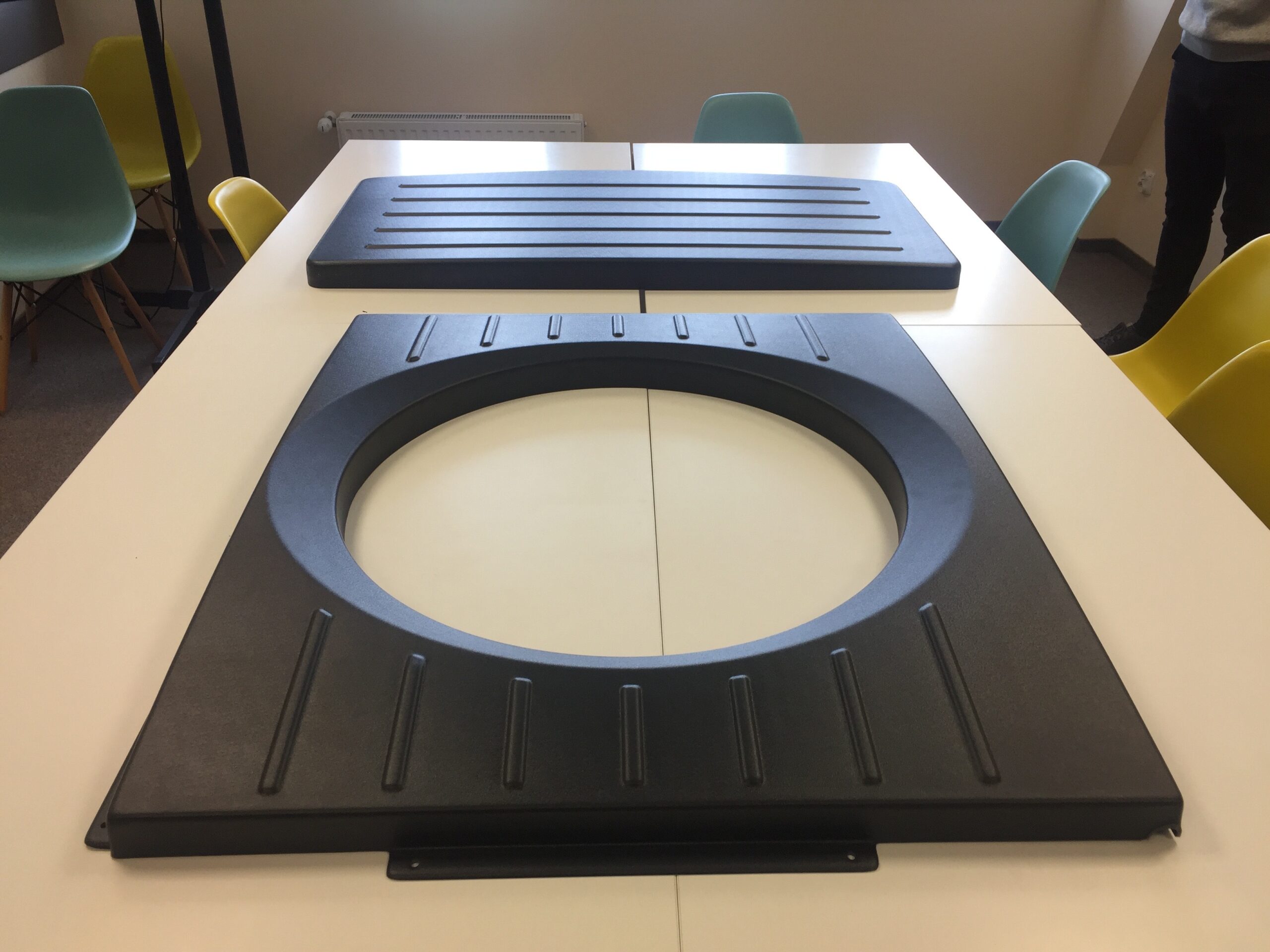
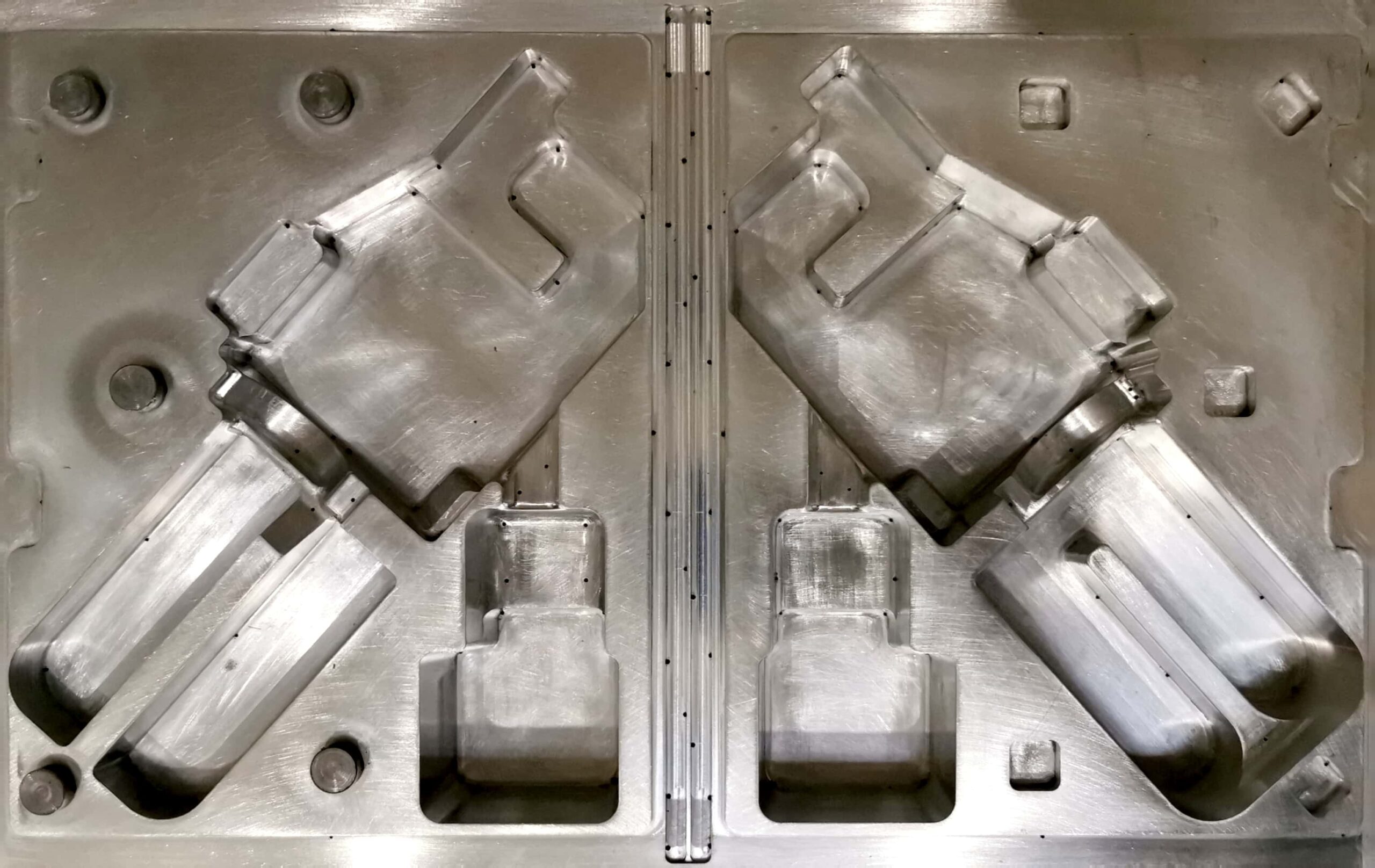
ABS material is one of the most commonly used plastics in the industry. This article describes its characteristics and when it is worth using.
By reading this article, you will learn:
- What is ABS material
- What are its advantages and disadvantages
- In which industries it is used.
What is ABS material?
ABS, or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is a popular polymer widely used in many fields. Due to its properties, this material is commonly used in industry, in the production of everyday items, and in prototype design. ABS is an amorphous material. The processing temperature of ABS is 190-260 degrees Celsius.
Extrusion, injection molding, and thermoforming are the technologies where ABS material is most commonly used.
Advantages and disadvantages of ABS material
Like every material, ABS has its advantages and disadvantages. Below we have described selected ones
Advantages of ABS
- high mechanical strength (which means it is resistant to impacts, vibrations, and wear)
- resistance to many chemicals, such as the effects of most acids, bases, and organic solvents, allowing it to be used in various environments where aggressive substances are present
- good dimensional stability (meaning it retains its shape and dimensions even with temperature changes)
- lower susceptibility to shrinkage and deformation compared to other plastics
- ease of machining and processing
- good insulating properties
- ease of coloring and giving various textures
Additionally, the advantages of ABS also include unique properties that characterize all plastics, such as low weight, low production cost, no corrosion, processing temperature, and the possibility of recycling. We have described this issue more extensively in a separate article.
Don't wait!
Tailor the technology to your needs to reduce plastic production costs.
Disadvantages of ABS
- poor resistance to sunlight, i.e., to UV radiation (with prolonged exposure to the sun, it may undergo degradation, change color, or lose some of its mechanical properties).
- During processing, ABS can emit volatile substances that may be harmful to human health or the environment.
- The allowable moisture content should be below 0.2% to avoid any negative impact on the quality of the final products. Therefore, it is recommended to dry ABS before processing. That’s why it’s a good idea to dry ABS before using it. Simply let it dry for 2-4 hours at a temperature of 75 degrees Celsius.
- despite its general resistance to many chemicals, this plastic can still be vulnerable to certain aggressive substances, such as certain organic solvents or strong chemicals.
- Compared to other materials, ABS is relatively difficult to recycle.
Furthermore, the use of ABS also comes with disadvantages that are common to all plastics, such as a lack of resistance to high temperatures, a long decomposition time, and its petroleum-based origin. We have described this issue more extensively in a separate article.
It’s important to note that some of the disadvantages of ABS can be mitigated. For instance, the issue of low UV resistance can be addressed by adding suitable stabilizers.
Applications of ABS
ABS is one of the most commonly used plastics. Below are some examples of its applications
Automotive industry
ABS has good thermal and acoustic properties, making it suitable for use as thermal or acoustic insulation in the interior of vehicles. It helps maintain a stable temperature and reduces noise generated by the engine and road. Its ease of coloring and painting allows for attractive and aesthetic finishes in cars. ABS can be used to manufacture various interior and exterior components, such as dashboards, door panels, overlays, and decorative details.
It is a relatively cost-effective material compared to some other materials like aluminum or carbon fiber. This makes it more accessible for automobile manufacturers, especially in mass production. ABS is a highly regarded material in the automotive industry due to its durability, ease of machining, insulation properties, aesthetics, and relatively low cost. It is used in the production of various automotive components such as covers, housings, moldings, panels, and interior elements.

Electronics
ABS has good insulating properties, which are crucial in electronics. It can provide protection against electrical conductivity and electromagnetic interference, which is essential for the safety and operation of electronic devices. It is used in the production of casings, panels, cables, shields, and other components in various electronic devices, from televisions and computers to audio-video and telecommunications equipment.

Prototyping
ABS can be easily machined and molded, making it an ideal material for prototyping. It can be injection molded, bent, 3D printed, milled, or cut to the required dimensions. This ease of processing allows for customization of ABS to meet various, even complex design needs.

Summary
ABS material is a versatile substance with numerous applications across various fields. Its unique properties, including strength, impact resistance, ease of processing, and insulation, make it a popular choice for many manufacturers and designers. If you have a project that requires a material with these qualities, ABS is worth considering.
Are you wondering if ABS material is suitable for your project? Consult your project with us, and our engineers will certainly advise whether ABS is the right material for your application.