Strona główna / Technologies / Thermoforming
Thermoforming of Plastics
Thermoforming is a technology that shortens the waiting time for producing plastic products and reduces tooling costs.
What is thermoforming?
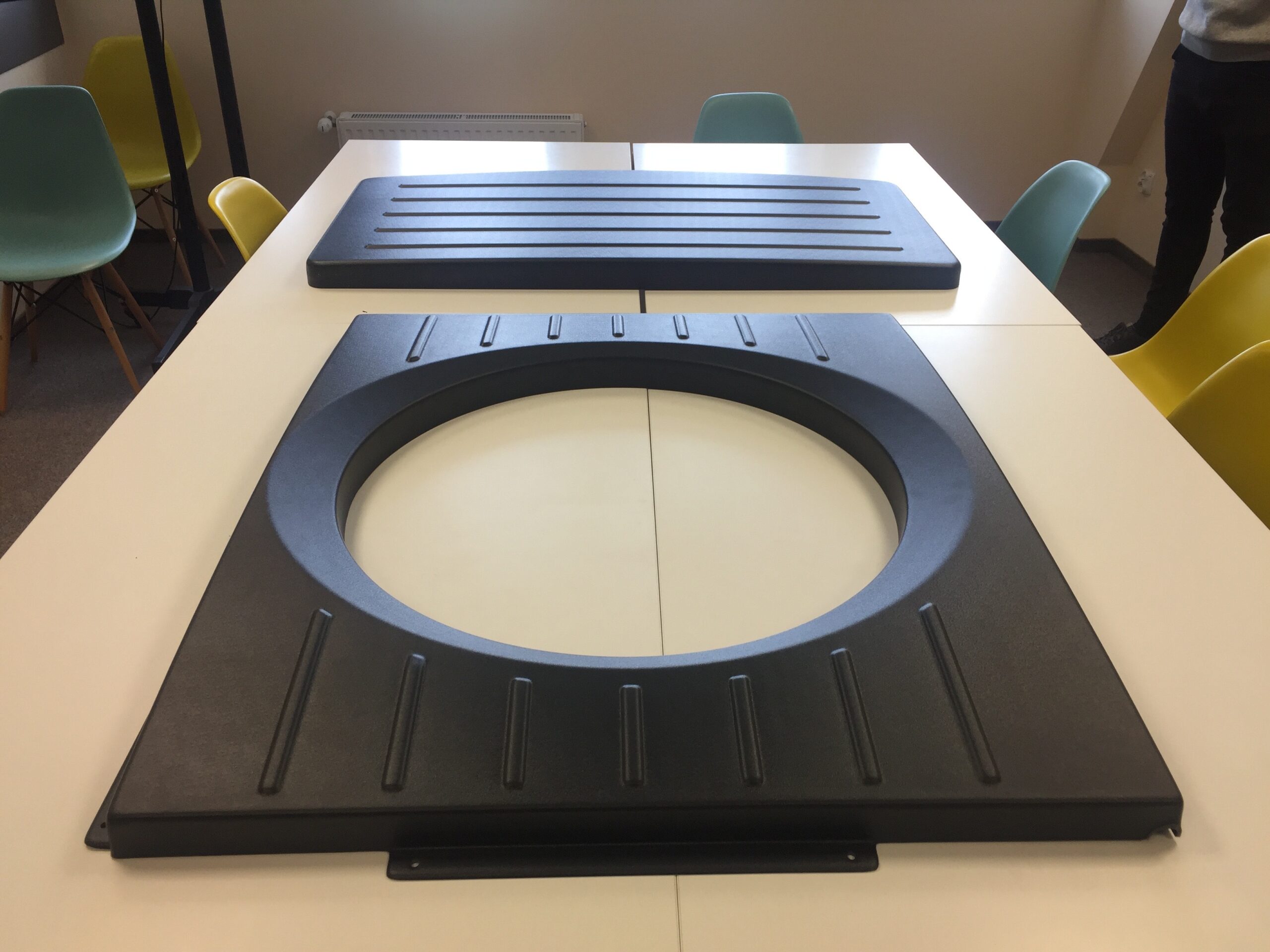
Thermoforming is one of the most versatile technologies for manufacturing plastic parts. It works by heating a sheet of thermoplastic until it softens to a malleable temperature (unique to the material), then shaping it into the desired form.
Plastic products made through thermoforming can have very thin walls.
Thermoforming also allows for rapid prototyping and reduces the costs of mold production.
Tooling is even up to 10 times cheaper than with other plastic processing technologies, such as injection molding.
Depending on the type of product to be created through
the thermoforming process, two methods can be used: negative and positive thermoforming.
The decision on which method to choose is based on factors like the anticipated variation in product wall thickness and which side of the item will be visible.
Dimensional tolerance of the produced shape is also significant. Thermoforming is a technological process that allows the use of multiple molds, enabling the production of many items in a single cycle.

What are some typical applications of thermoforming?
Disposable cups
Containers
Lids
Trays
Blisters
Products for the food industry
Products for the medical industry
General retail goods
Vehicle door panels and dashboards
Refrigerator linings
Commercial vehicle beds
Plastic pallets



What materials do we use
in thermoforming?
Styrenic plastics are most commonly used in thermoforming.
These include materials like PS (polystyrene) or ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene).
ABS as regrind.
Materials used in thermoforming also include polyolefins such as PE (polyethylene) or PP (polypropylene), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), and biodegradable plastics like PLA (polylactic acid).
It’s important to note that while thermoforming provides a broad selection of raw
materials, it also tends to produce substantial waste from trimming excess material. Consequently, the cost of the raw materials plays a significant role in this technology.
How does the thermoforming process work?
Thermoforming proceeds in four stages.
Machine programming
We set up your mold and program the thermoforming machine according to the desired parameters, such as oven temperature and heating time.
Heating the thermoplastic sheet
Next, the plastic sheet is placed in the oven to be heated. After reaching a temperature that allows for material molding (slightly above its plasticity threshold), it is removed from the oven, placed on the mold, and air is vacuumed through holes in the mold, causing the sheet to take the shape of the mold.
Forming
Before removing the part from the mold, some time is needed for the plastic to harden. Typically, several test cycles are required to adjust various parameters such as temperature, cycle time, and other forming requirements.
Process parameter control
Every part and product is meticulously checked to ensure clean formation and adherence to specifications, as well as the maintenance of optimal process parameters. These include the temperature of forming, mold tool temperature, vacuum and air pressure, and the flow rate and temperature of cooling fluids or air.
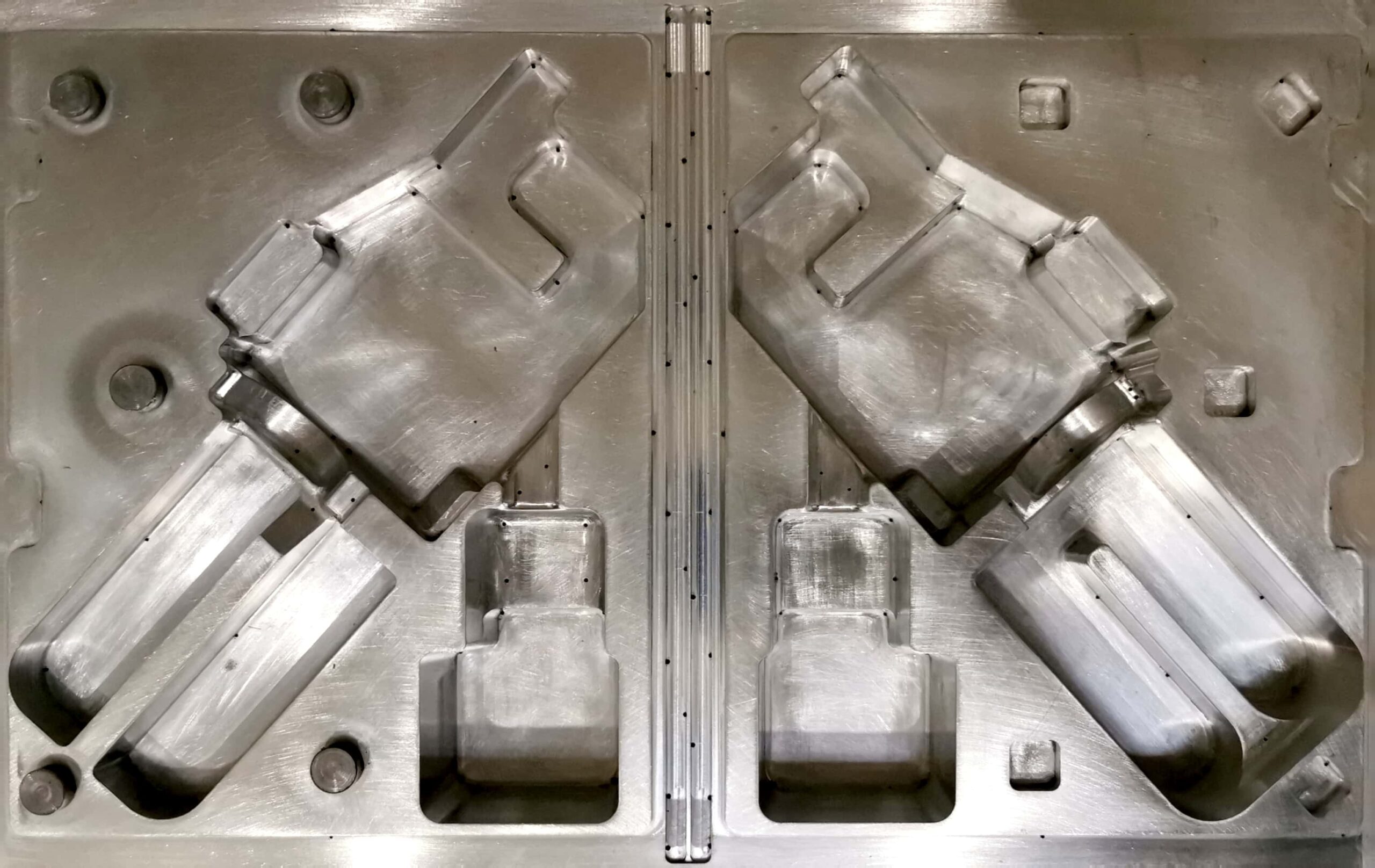
What types of molds are used in the plastic thermoforming process?
The type of mold used in plastic thermoforming
depends on the required production accuracy. When the highest quality and precision of the product are critical, and long-term mold use is desired, aluminum molds are preferred.
In other cases, wooden molds, wooden
molds covered with composite, plaster molds, or polymer resin molds are perfectly suitable. Such molds are less expensive to make, the quality of the products is good, and the molds work well for short production runs.
Plastic Processing at Plastipol
Thanks to our extensive technological capabilities – we are able to realize almost any plastic project.We utilize 4 production technologies – injection molding, extrusion, rotational molding, and thermoforming..
Understanding the application of the product, we can also properly advise changes to adapt the technology to the project. We ensure that the chosen production technology is optimal in terms of both technological and economic aspects. Our modern machinery plays a significant role in helping us produce top-quality plastic products.

What are the advantages of thermoforming?
- the ability to produce large surface area products with thin walls
- low mold costs
- the ability to use multiple molds, increasing production efficiency
- freedom in choosing the raw material for forming
- the ability to quickly produce small production runs from various materials
- various thermoforming methods are available, which are used depending on the conditions of plastic processing: vacuum forming, pressure forming, and twin-sheet forming.
Frequently Asked Questions
Thermoforming is a flexible technique that can produce a range of items, from thin-walled trays and blisters to large-scale machinery parts. It’s suitable for any item that needs an even wall thickness and can be shaped over a mold. Its applications are varied, including:
- covers
- housings
- blisters
- trays
- packaging
Thermoforming is a flexible technique that can produce a range of items, from thin-walled trays and blisters to large-scale machinery parts. It’s suitable for any item that needs an even wall thickness and can be shaped over a mold. Its applications are varied, including:
- covers
- housings
- blisters
- trays
- packaging
The costs for wooden molds start from a few hundred PLN. For aluminum molds, it’s usually around several thousand PLN. In the case of mass production of numerous low-thickness elements, molds can cost tens of thousands of PLN.
Thermoforming proceeds in four stages:
- Machine Programming – We set the mold and program the thermoforming machine according to the desired parameters.
- Heating the Thermoplastic Sheet – We place the plastic sheet in the oven to be heated.
- Forming – After reaching the temperature that allows material forming (just above its plasticity threshold), the sheet is removed from the oven, placed on the mold, and air is vacuumed through the mold’s holes, shaping the sheet into the mold. Before the part is removed from the mold, there is a waiting period for the plastic to harden.
- Process Parameter Control – All parts and products are meticulously inspected to ensure they are cleanly formed, meet specifications, and maintain optimal process parameters.