Strona główna / Technologies / Injection Molding
Injection molding
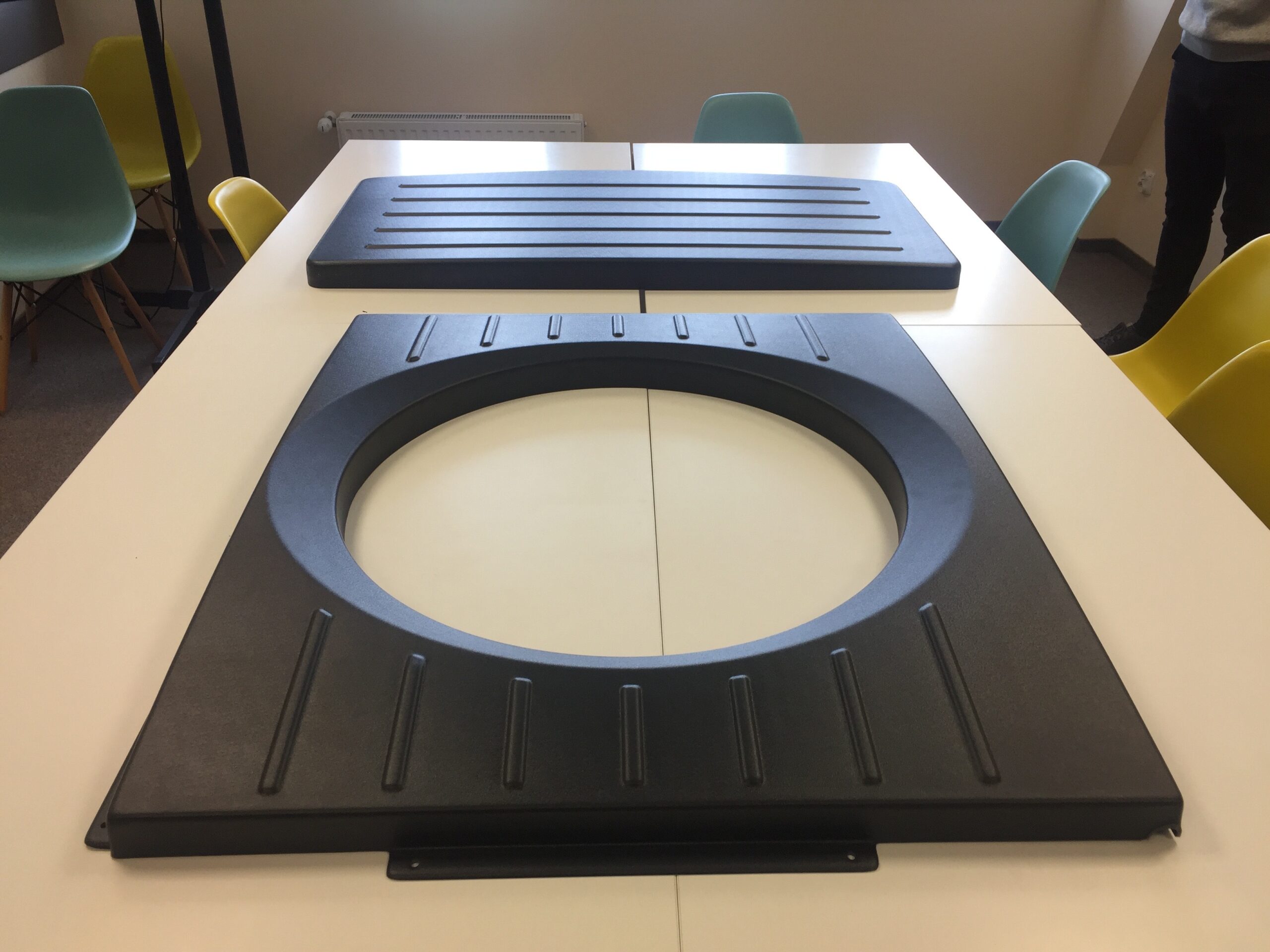
Injection molding is one of the most efficient and commonly used methods for producing simple as well as complex plastic products . Injection molding is particularly cost-effective for mass production.
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a plastic molding technology that offers a vast spectrum of possibilities. How does the injection molding process work? Plastic injection molding works by melting plastic granules and then injecting them into a mold under high pressure and temperature. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, it’s ejected as a finished piece. Injection molding is widely used to manufacture a variety of parts, from the smallest components to car body panels.
One of the techniques used in plastic injection is insert molding, which allows for embedding multiple materials in a single part by injecting and filling the mold with inserts. In this process, preformed or machined components can be placed into the mold, allowing the injected material to mold and solidify around them. The injection time depends on the size of the product, the type of material, and the efficiency of the injection machine. Meanwhile, the quality of the resulting products depends on factors such as the design of the injection mold used in the plastic injection process.
What are example applications?
Fax connectors 48
LEGO bricks
Enclosures
Packagings
Rubber to metal bonding
Rubber components
Automotive industry components
Components for consumer electronics and appliances
Fittings
Everyday use items
Bottle caps
...and many more!



What materials are used in injection molding?
Injection molding allows the use of a wide range of polymers and thermoplastics. This includes polymer resins, all kinds of thermoplastics, some thermosetting materials like epoxy and phenolic, and elastomers. Thermoplastics like nylon, polyethylene, and polystyrene are particularly popular due to their recyclability, versatility, and ability to soften under heat. The choice of materials is based on factors like cost, strength, flexibility (how much a material can bend without breaking), resistance to heat deformation, and water absorption.
How does the injection molding process work?
Injection molding process proceeds in four stages:
Heating and liquefying the plastic
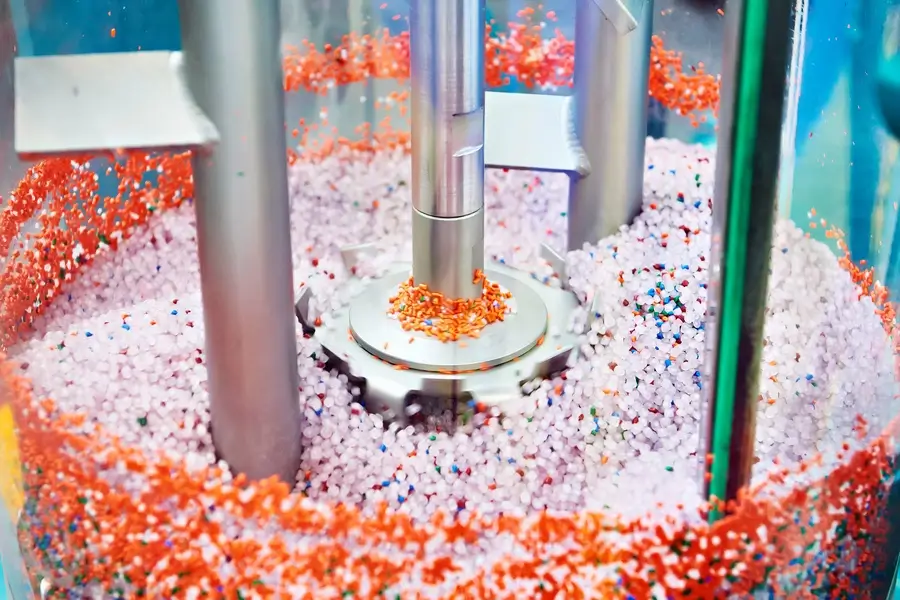
Pre-dried granulated plastic is fed through a hopper into the heating chamber by a piston. The granules are gradually moved forward by the rotating motion of the screw, then the plastic is pushed into the heated chamber where it melts.
Injection of the plastic
As the screw moves forward, the melted plastic is pushed through a nozzle that presses against the mold, allowing it to enter the mold cavity through a gate and runner system. The material is then injected at high pressure into the mold, giving the polymer the desired shape. The mold remains cold, so the plastic solidifies almost immediately after the mold is filled by the packing pressure.
Cooling the mold at the appropriate temperature
The molded parts in the filled mold cavities are cooled using a selected heat exchange medium (water, air). The cooling time is about 30-50% of the injection cycle time.
Emptying and closing the mold
After the parts cool down, they are removed from the mold, which is then closed for the next production cycle.
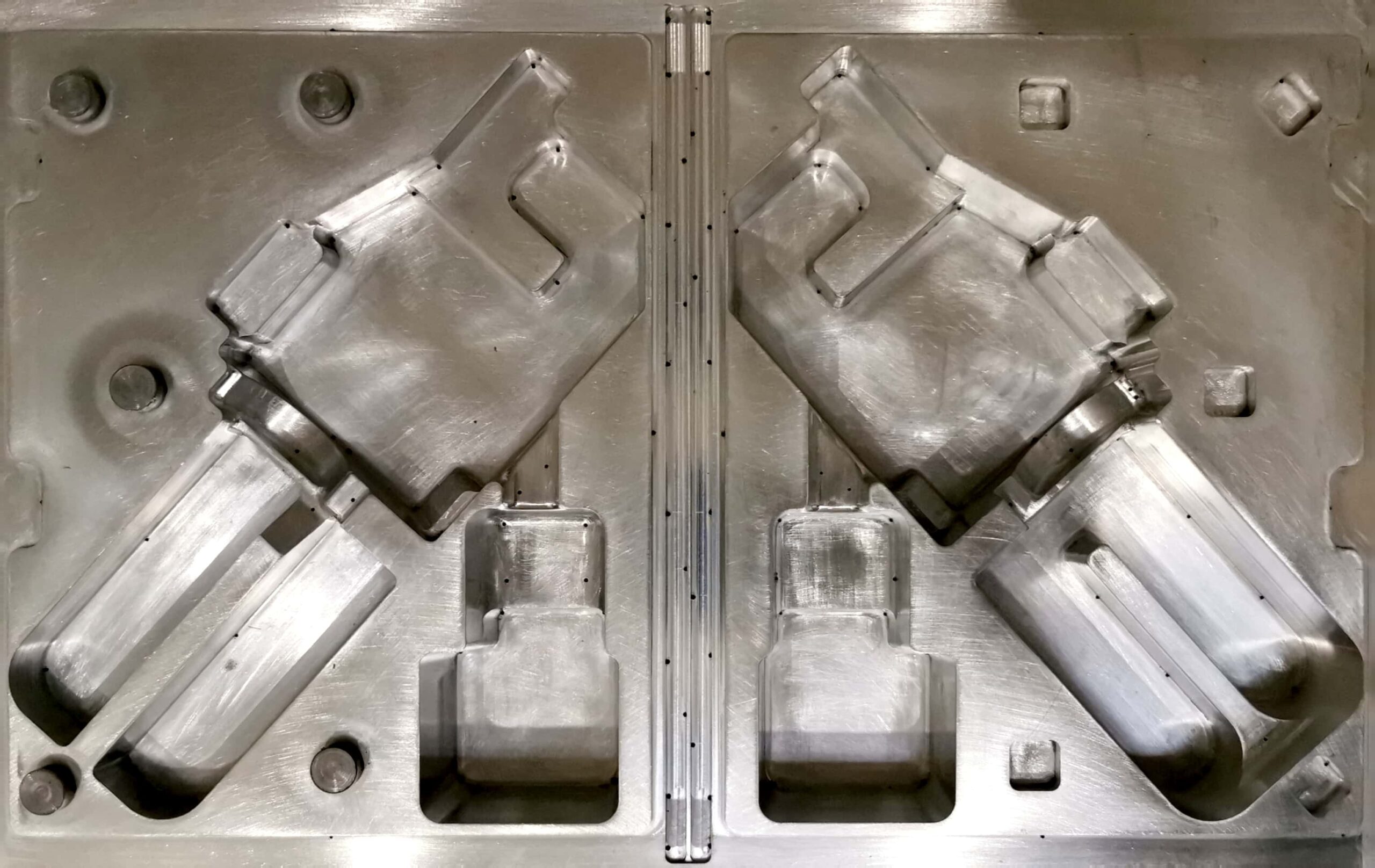
What types of molds are used in plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding requires the use of a complex mold. The molds used in plastic injection molding are typically made of tool steel, but stainless steel and aluminum molds are also suitable for certain applications. Aluminum molds have poorer mechanical properties and are more prone to wear, damage, and deformation during injection and clamping cycles. We also facilitate injection with inserts, allowing a permanent connection of the insert with another material. This solution is useful in producing plastic parts with protruding metal screws, like keys. Injection molding is characterized by high tooling costs, making it uneconomical for short production runs. It is much more cost-effective for mass production.
Replaceable
molding inserts
In some cases, instead of an entire mold, we can use replaceable molding inserts, significantly reducing the initial cost. This solution is applied for small and medium production runs.
What surface finish can the produced parts have?
Depending on the needs, the finished products can have different surface finishes. It results from the structure used on the mold. It can be:
- Technical polish, which is the surface obtained directly after milling
- Mirror polish – a smoother surface than technical polish, until a mirror-like effect is achieved.
- Textured surface – various treatments are applied to create different textures that affect both aesthetic and functional aspects, such as sandblasted surfaces.
More...
Injection molding of plastics allows for the production of several different parts in one mold. However, this solution is rarely used due to its limitations. The products must have similar mass, and the production cycle time must be close.
It is also possible to create a component consisting of two different plastics. The process involves two stages: first, one material is injected, and then it is overmolded with another material.
What are the advantages of injection molding?
the ability to manufacture highly complex products in a single technological operation
we obtain a finished product ready for use, virtually without finishing machining
high quality, repeatability of shape and dimensions, product aesthetics
the possibility of full automation and computerization of the process
the ability for mass production
low labor intensity
low emission of harmful substances
We use 4 production technologies
Thermoforming
Technology to reduce the time it takes to manufacture plastic products and reduce tooling costs.
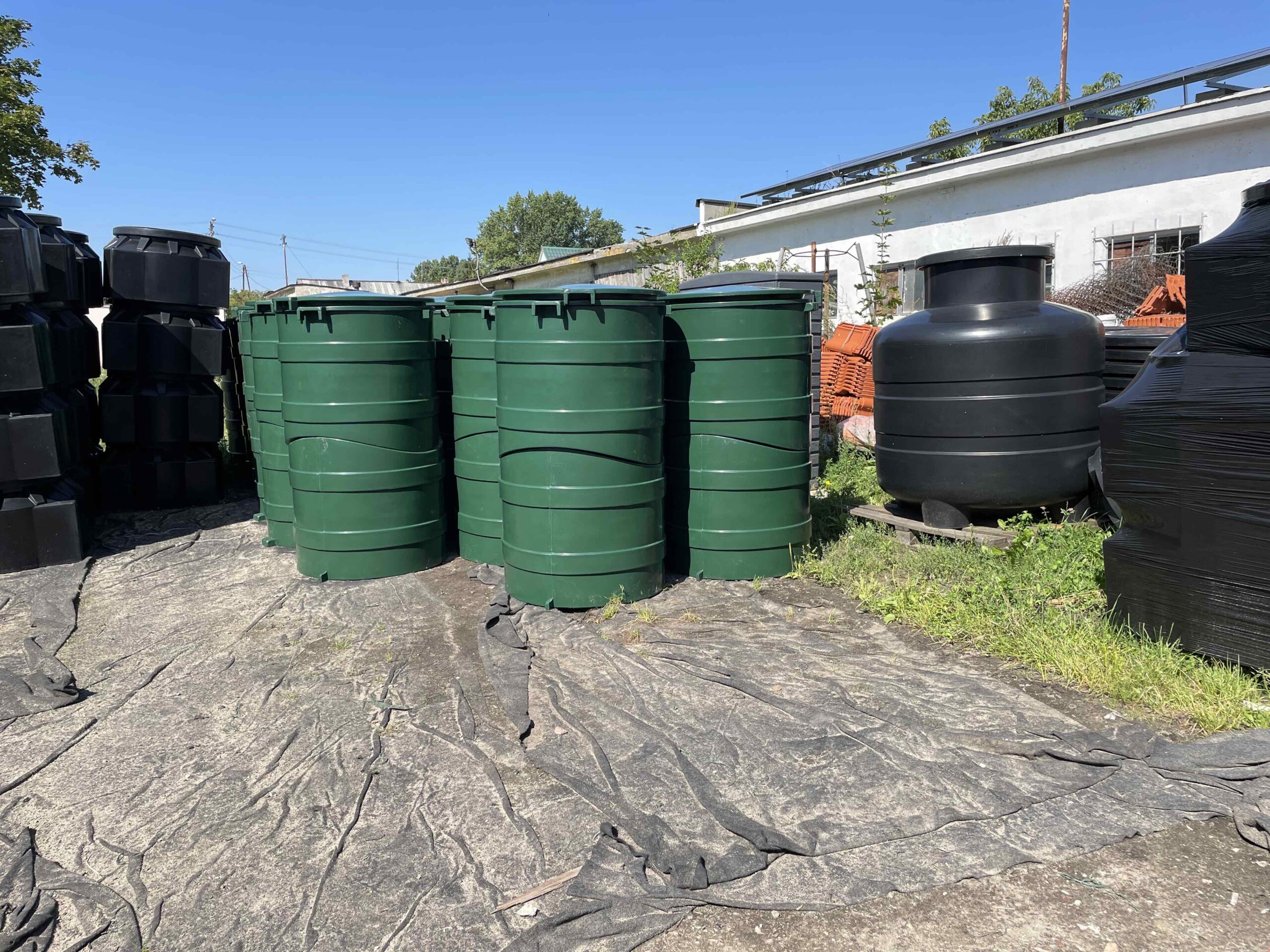
Rotational moulding
Ideal technology for manufacturing large-scale plastic products.
Example application:
- containers for fuel or chemicals
- industrial tanks
- containers for food or water
- canoes and boats
- safety helmets
Injection molding
One of the most efficient and most widely used methods of producing simple as well as complex plastic products.

Example application:
- components of household appliances and consumer electronics
- enclosures
- bottle caps
- everyday use items
Extrusion
Ideal technology for large production runs of long components, such as profiles, pipes or gaskets.

Frequently Asked Questions
In the plastics processing industry, injection molding is an ideal technology for medium, large, and very large production runs. Plastic molding is a highly efficient and versatile technology in which most plastic components can be produced, including:
- enclosures
- fittings
- packagings
- everyday use items
- machine and equipment components
Injection molding of plastics is economically efficient for large-scale production.
The cost of an injection mold typically starts from tens of thousands of PLN. Sometimes, for complex multi-cavity molds, this cost can exceed one hundred thousand PLN.
Injection molding process proceeds in four stages:
- Heating and liquefaction of the material. Pre-dried granulated plastic is fed into the heating chamber, where it is melted.
- Injection of plastics. The raw material is injected at high pressure into the mold, giving the polymer the desired shape. The mold remains cold, so the plastic solidifies almost immediately after the mold is filled by the packing pressure.
- Cooling the mold at the appropriate temperature. The formed products in the filled mold cavities are subjected to a cooling process using a selected heat exchange medium (water, air).
- Emptying and closing the mold. After the parts cool down, they are removed from the mold, which is then closed for the next production cycle.