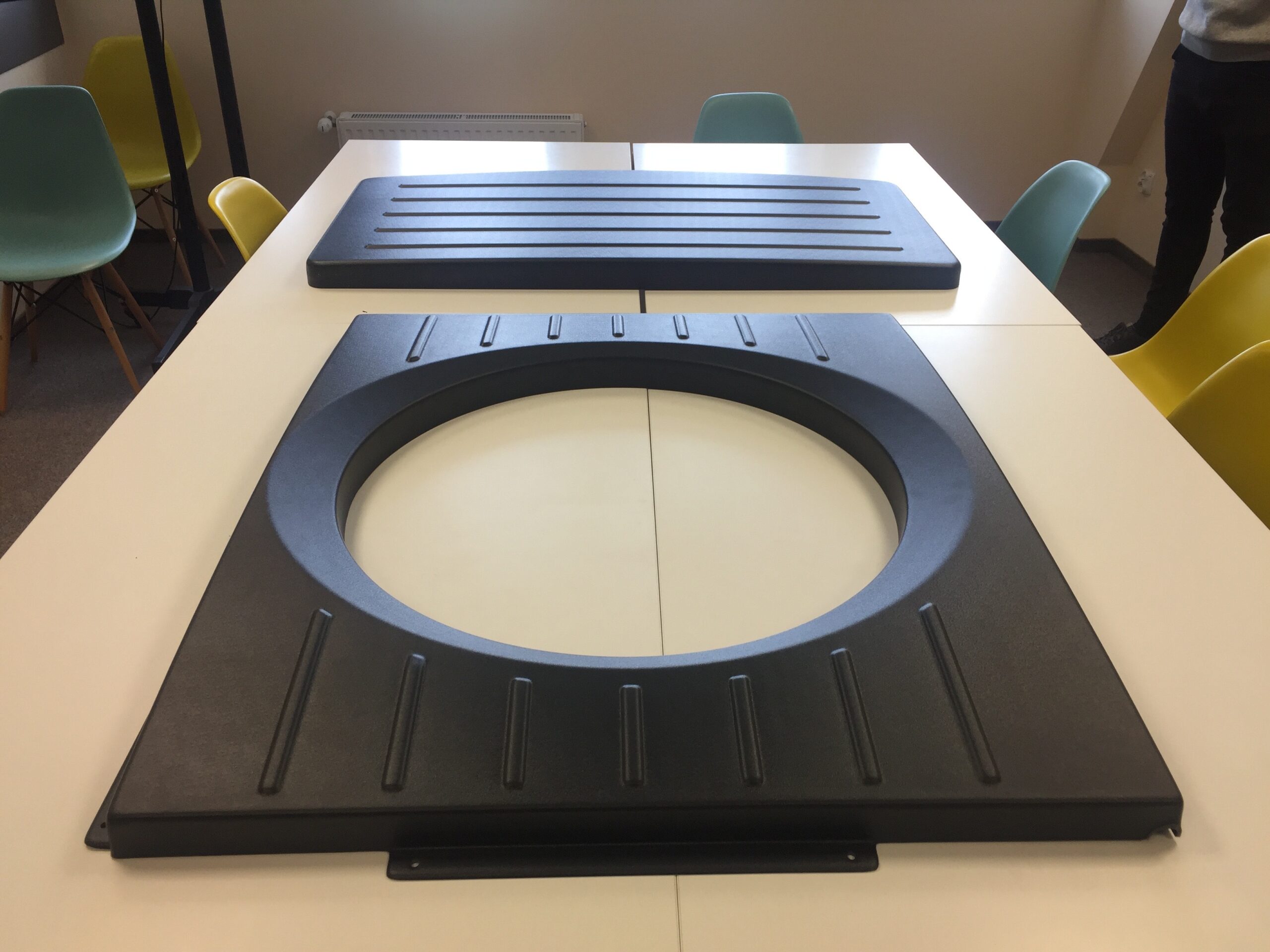
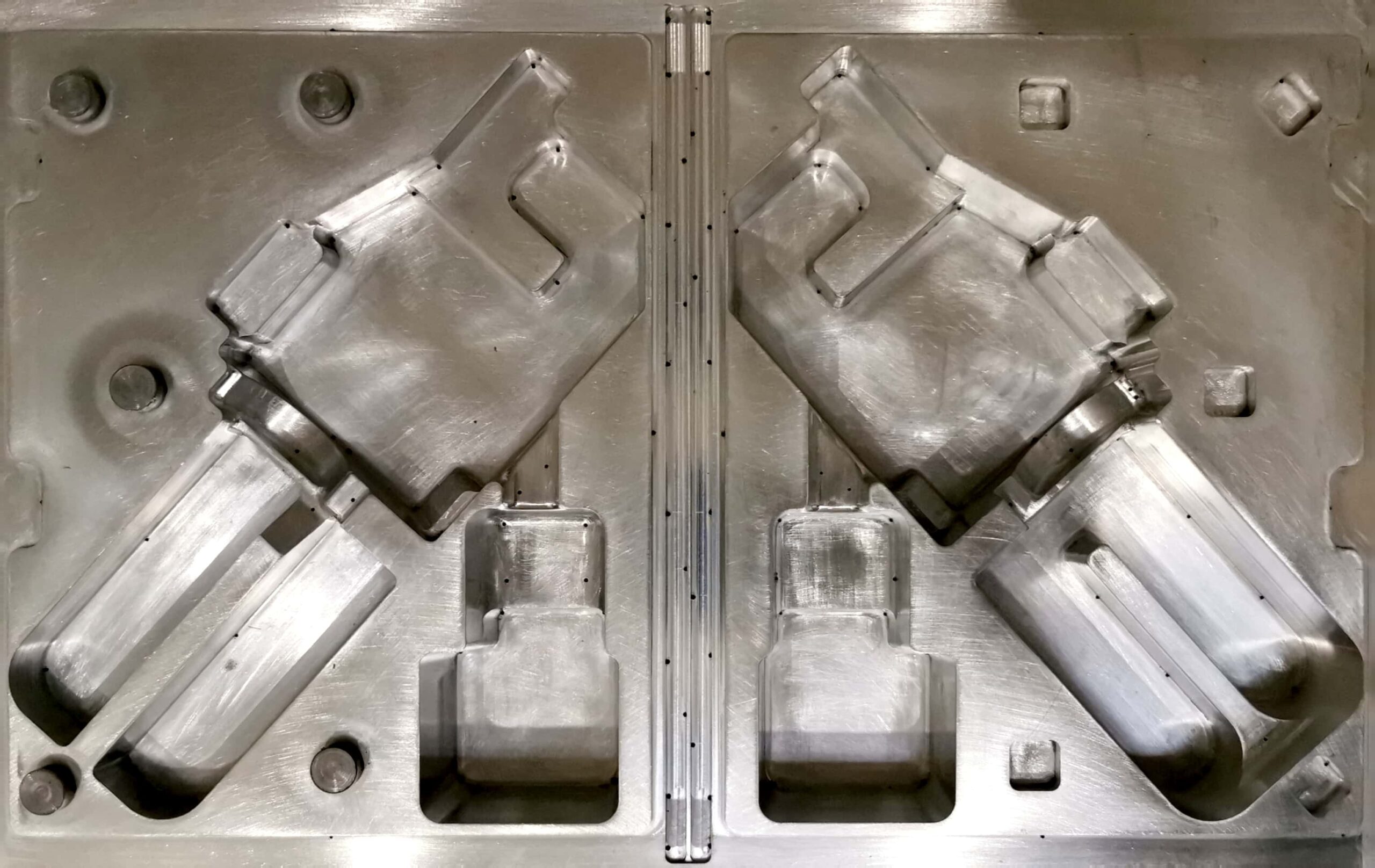
Thermoforming is a technology for producing open products with uniform wall thickness, such as lids, containers, housings, but also blisters or trays. In order to make parts using thermoforming technology, it is necessary to make a mold beforehand, which is the necessary tooling.
Depending on the application, size, or quantity, there is a wide variety of materials from which we produce thermoforming molds. Their main advantage is that tooling can be up to 10 times cheaper than other plastic processing technologies (such as injection molding).
In this article, we describe, from the practical side, how moldmaking works and what materials to use for different implementations.


Thermoforming of plastics – a brief overview.
Thermoforming is a very versatile technology for manufacturing plastic products. It involves heating the thermoplastic sheet first to a certain temperature, and then forming it into the desired shape, on a pre-made mold.
The input material is board or film. You can learn more about thermoforming technology on a dedicated subpage and blog post.
What kind of products can be created by thermoforming?
Products that are created by thermoforming technology have a very wide range of industrial applications. These may include:
- Covers
- Containers
- Enclosures
- Packaging
- Blistry
- Components of machinery and equipment
- Trays
- Shields
- many, many more…
Molds for thermoforming – characteristics.
Mold manufacturing is an essential step before the thermoforming process.
The main requirement for the molds is that the plastic be able to form properly on them. This occurs by aspirating the material. Therefore, it is important to make the molds to the correct tolerance, as this will affect the dimensions of the final product.
In order to maintain dimensional repeatability, stability of the molds is essential, as the molds heat up during the thermoforming process.
Molds for thermoforming are usually cheaper and simpler to produce than tools for other technologies. The cost of the moldalso dependson the size and complexity of the product, but is usually about 50-90% lower than in injection molding technology.
Type of mold used for thermoforming plastics
depends on the required accuracy, demand, size and complexity of the product.
Thermoforming molds have openings that are used to drain air. They are small enough not to be visible on the product.
Types of molds for thermoforming.
There are several methods of manufacturing thermoforming molds, as well as the materials from which they can be made. This chapter describes a selection that is often used in the industry.
Materials
The most commonly used materials for thermoforming molds are:
Don't wait!
Tailor the technology to your needs to reduce plastic production costs.
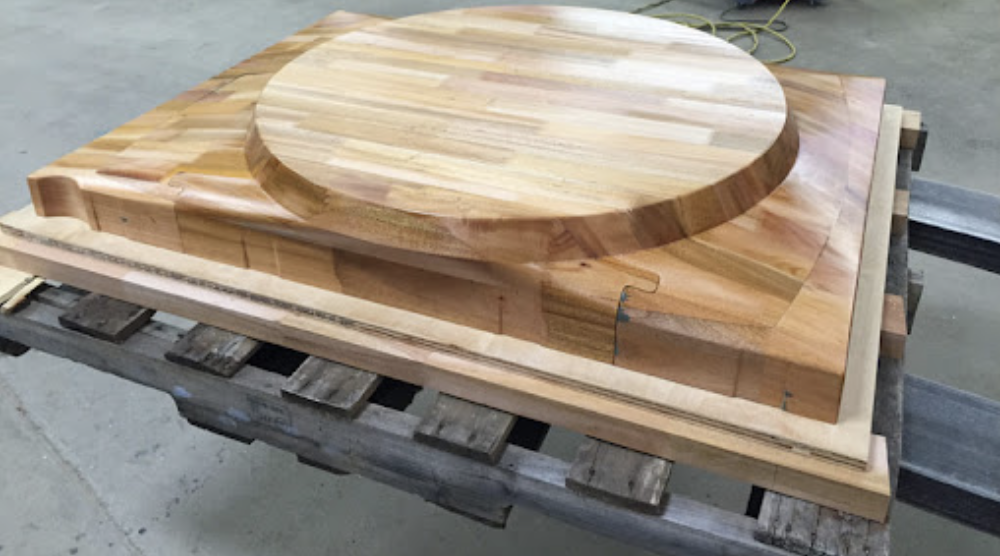
Wood (MDF)
MDF material molds have a low manufacturing cost, which is especially important for larger products. They are mainly suitable for simple shapes, where very high manufacturing accuracy is not required.
We cover wooden molds with impregnation and composite.
We mostly use them for prototypes, as well as smaller production runs.
MDF molds can also be used as a “backhoe” for casting with other material, such as. resin.

Resin
Resin molds are more durable and more expensive than MDF molds. We mostly use them for small and medium production runs. The implementation consists of two stages:
- Produce a pre-mold (e.g., from MDF)
- Making a “hoof” and then casting a resin mold. It is important to consider appropriate shrinkage in casting to maintain dimensional tolerances.
Plastics
Thermoforming molds can also be made of plastic (made by CNC machining). It is an alternative to resin molds. Plastics can also be 3D printed, although this is mainly applicable to prototypes.
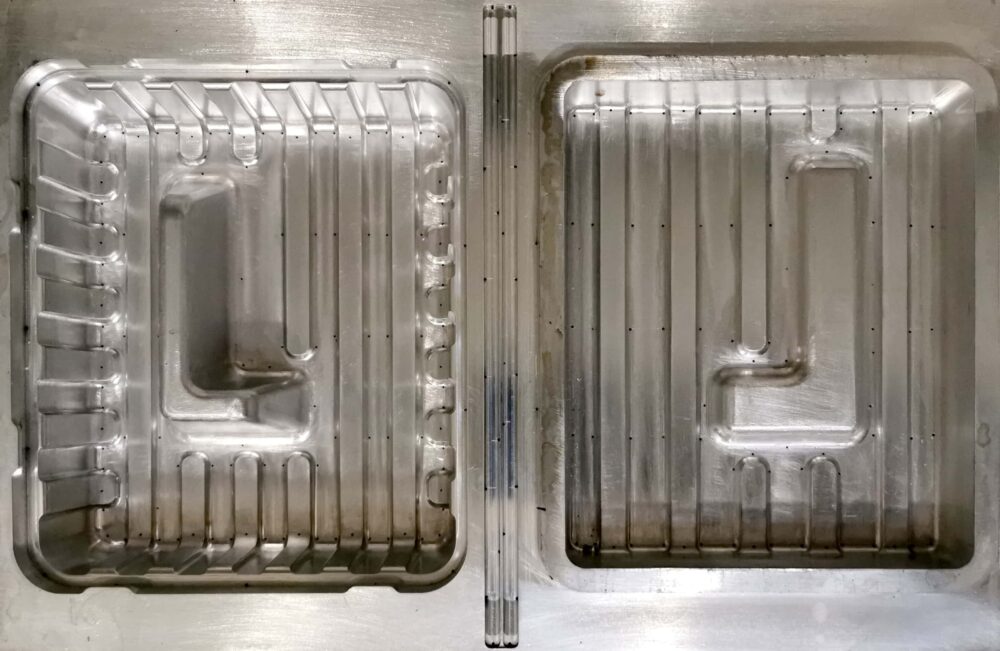
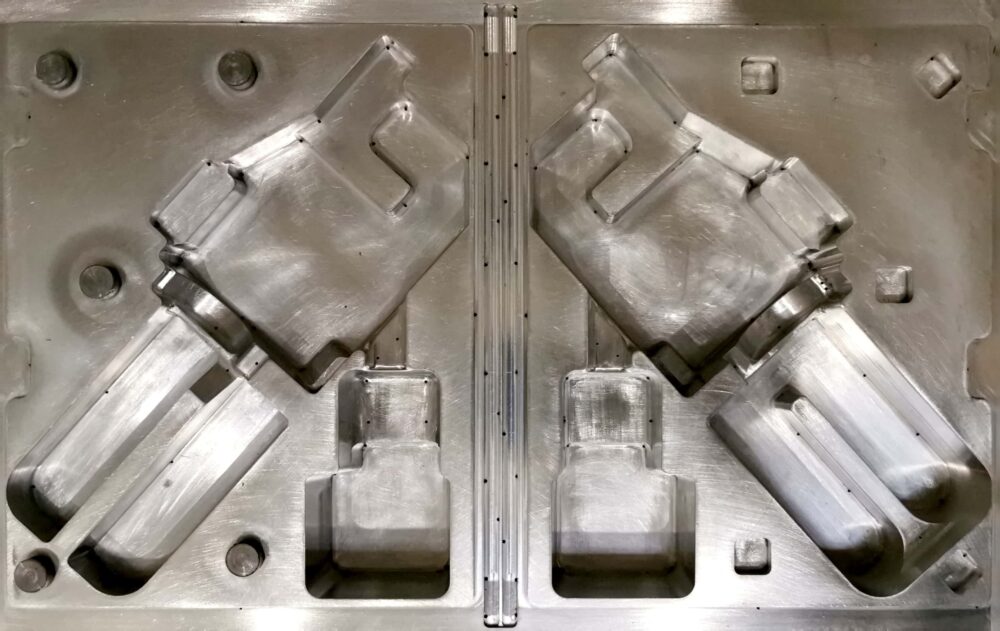
Aluminum
Aluminum molds are the most commonly used by us. They are used for medium and large production runs. Aluminum molds have many advantages, including:
- good thermal conductivity
- high durability
- attractive price in relation to features
- good dimensional stability
Products made on aluminum molds allow high accuracy and repeatability, and production is efficient.
Aluminum is a very good conductor of heat, which is crucial for the thermoforming process.
Aluminum molds are also suitable for blister production.
Steel
Steel molds are used for highly efficient high-volume or mass production of small-wall-thickness parts, such as blisters. The molds consist of many components. Tooling has a high price, and production is very efficient, which positively affects the price of manufactured parts.
Production methods
Molds for production in thermoforming technology are not as complicated as, for example, in injection molding technology. The most commonly used production methods:
CNC machining
The most common way to produce thermoforming molds is CNC machining. This is the default manufacturing method. During production, vents can be easily added to remove air, and the minimal porosity of the mold allows for high precision detailing.
CNC machining involves the proper removal of material from a larger piece/block.
Aluminum can be processed, as well as wood or plastic.
Casting
Casting involves the creation of a suitable mold (hoof) into which the material is poured, which then solidifies.
Resin can be cast, and the process is described in the paragraph on resin molds.
The cast aluminum is melted and molded into the shape of a mold.
Don't wait!
Tailor the technology to your needs to reduce plastic production costs.
3D Printing
3D printing is the least commonly used method for producing thermoforming molds. It has its uses practically exclusively for prototypes.
Molds for thermoforming – breakdown
Choosing the right material and mold making method depends on several factors. The most important of these is production volume.
Prototype molds
When producing prototypes, the most important thing is to minimize costs so that, if necessary, several different molds are made before a satisfactory result is obtained. For this reason, we most often use molds of machined MDF.
Molds for mass production
For mass production, we usually use molds made of machined aluminum. Depending on the volume of production and the complexity of the product, we may also use a different material (e.g. resin, plastic, MDF), as well as the production method (e.g. cast aluminum).
Molds for mass production
In thermoforming technology, mass production refers to thin-walled parts, such as blisters. For such production, all tooling made of different steel alloys is used to ensure the highest efficiency.
Thermoforming molds – prices
The cost of molds depends on many factors, including. size, required dimensional tolerance, shape, etc. Below are the forks that apply to most “standard” implementations:
- The cost of wooden molds usually ranges from several hundred to 1.5-2 thousand zlotys net.
- Resin molds are usually a net cost of 2-4 thousand zlotys.
- Aluminum molds, is the cost of the order of 4-10 thousand zlotys net.
- Steel tooling for mass production is a cost starting at tens of thousands of zlotys.
Making a prototype before mass production.
To make a prototype, it is necessary to make a mold beforehand. However, there is a way (often used by us) that allows you to make a prototype at a lower cost.
The target material for mass production is usually aluminum. Often we suggest making a wooden mold (MDF) beforehand, the cost of which is an order of magnitude lower. We work on such a prototype form until we get a satisfactory result. The next stage is already making the target mold, for efficient mass production.
Another solution is to first make a prototype mold and then use it to make a “backhoe” from which the target mold will be cast. Note, however, that there are casting shrinkages that affect the dimensions. For this reason, it is rarely used by us.
Summary
Thermoforming is a technology that is widely used in industry. Inherent in this are the molds, the making of which is necessary to start production.
The cost of the molds is relatively low, compared to other technologies, which lowers the entry threshold for launching production.
There are both a variety of materials and production methods for thermoforming molds. Depending on the individual project, we make the appropriate choice based on factors such as implementation cost, production volume, efficiency, required accuracy, etc.
Thinking about, manufacturing with thermoforming technology? Consult your project with us, and we will advise you on the best material to make a mold for your project.