Plastic is everywhere in our lives, from daily objects to complex parts. This versatile synthetic material plays a crucial role in many fields, but it is also becoming the subject of increasing attention due to its impact on the natural environment. In this article, we will take a closer look at this fascinating material.
Reading the article, you will learn:
- Plastic, synthetic materials – what are they and what groups do we distinguish?
- What does the plastic production process look like?
- The most important characteristics and uses of plastics.
- Why is plastic so widely used in industry?

What is plastic?
“Plastic” is a general term, a colloquial expression that covers a wide range of synthetic materials.
These materials are composed of polymers. A polymer is a chemical substance with a high molecular weight, made up of long chains of repeating units known as monomers. These monomers join together in a process called polymerization to create a polymer. Plastic can vary in form, ranging from soft and flexible to hard and stiff.
The most important characteristics of each group of synthetic materials
There are many classifications of synthetic materials. Below, we focus on a few of the most important ones:
Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Polymers
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are a group of materials characterized by their ability to become soft and pliable when heated to the right temperature, making them easy to mold. Once the heat source is removed, they return to their original state. They can be molded multiple times without affecting their properties. Examples of thermoplastic polymers include: PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), and PS (polystyrene).
Thermosetting polymers
These are polymers that become soft and pliable under the right temperature and eventually harden over time. Duroplasts cannot be reprocessed. Examples of duroplastic polymers include: EP (epoxy resin), PEC (polyacetylene), and PAN (polyacrylonitrile)
Natural and synthetic polymers
Artificially modified natural polymers
Modified polymers are a group of substances that naturally occur in nature and are only modified by humans. Examples of natural polymers include cellulose, chitin, and natural rubber.
Synthetic polymers
Synthetic polymers do not occur naturally in nature; they are obtained through artificial human actions. Examples of synthetic polymers include PE (polyethylene), PS (polystyrene), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and PU (polyurethane).

Plastomers and elastomers
Plastomers
These are polymers that exhibit small deformation (below 1%) under the influence of stress. Examples of plastomers include: PE (polyethylene), PP (polypropylene), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and PS (polystyrene).
Elastomers
They are polymers that exhibit large deformations (100% and more) under the influence of stress. Examples of elastomers include: Natural rubber and polyurethanes (PU).
How does the production of plastic look like?
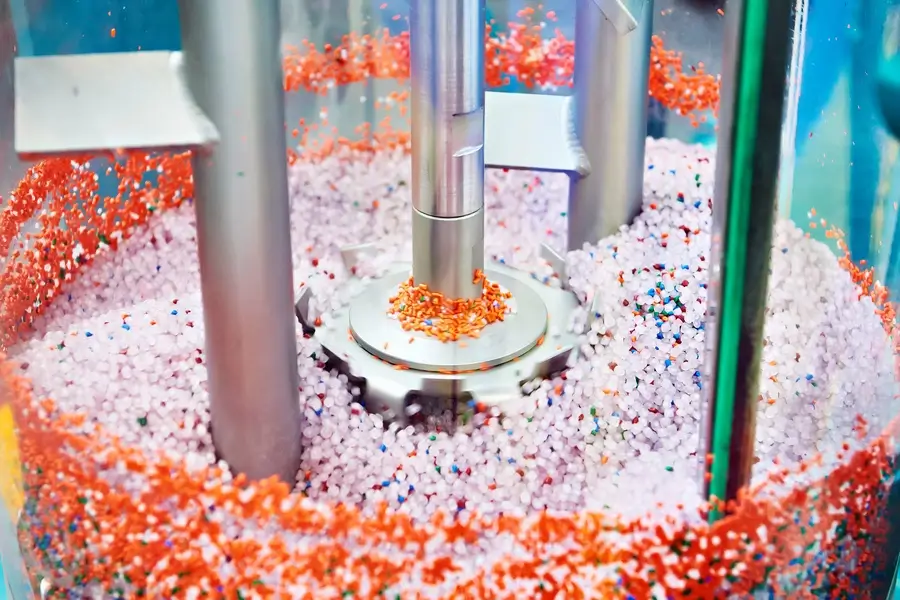
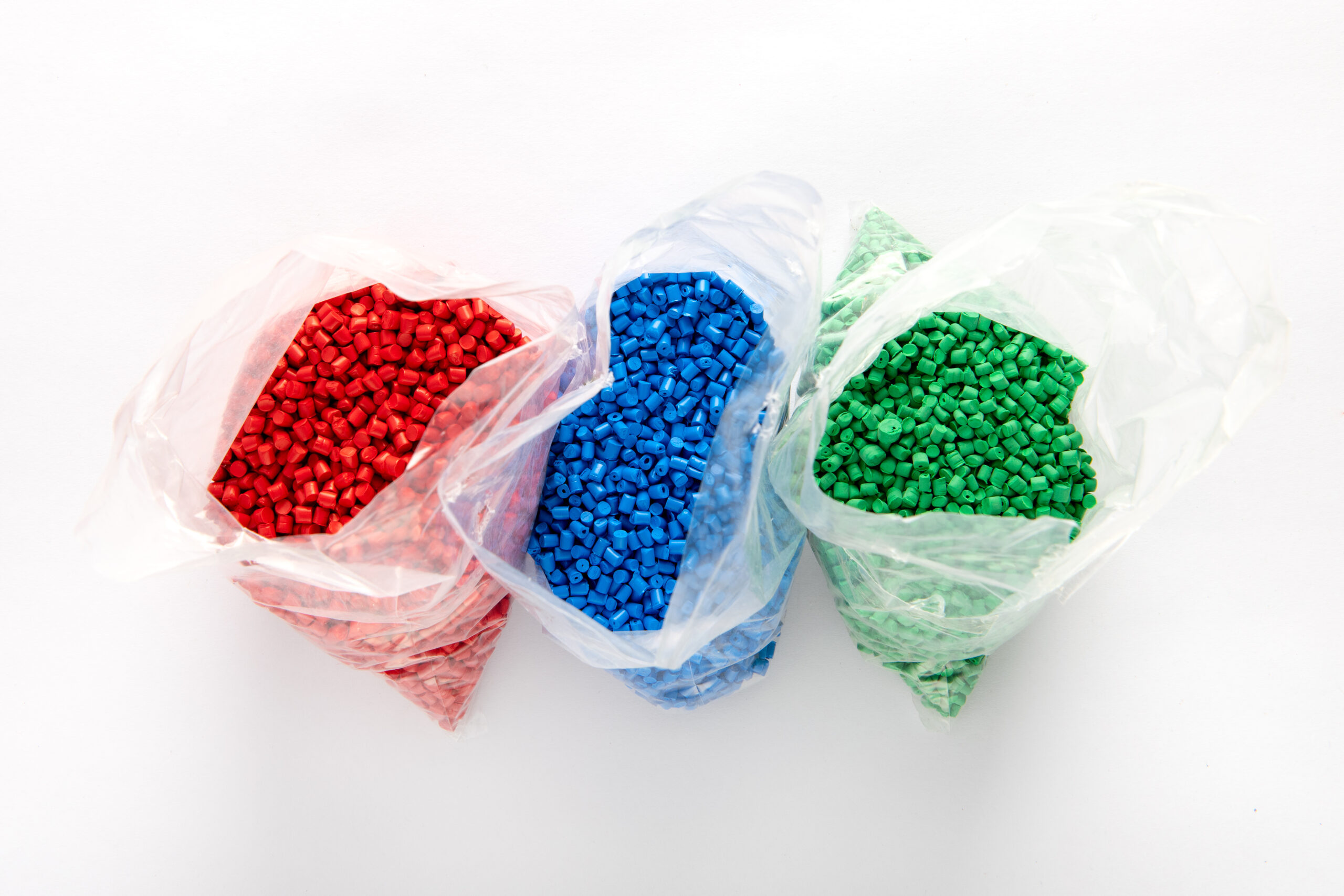
Plastic production can occur naturally or artificially. In natural production, plastic raw materials are obtained from natural sources, such as plant rubber or amber copolymers.
However, most plastics are produced artificially. This process involves combining monomers into long polymer chains using chemical processes such as polymerization. This allows for a wide range of plastics with varying properties to be produced.
The most important characteristics of plastics
Plastics are characterized by various specific properties that make them suitable for different applications.
Examples of unique properties of plastics include, for example:
- corrosion resistance
- lightweight
- ability to modify the structure
- mechanical strength
You can read more about the advantages and disadvantages here.
Why is plastic widely used in the industry?
Plastic is commonly used due to its versatility and low production cost.
It can be molded into various, even complex shapes, making it ideal for the production of various products, from packaging to automotive parts.
Furthermore, plastic is lightweight, which reduces fuel consumption in transportation and makes it easier to use many everyday items.
Below are the key characteristics for which polymer materials are frequently used in the industry:
High durability and resistance -> many types of plastics are resistant to atmospheric conditions (including sunlight) and moisture. Additionally, they are not susceptible to corrosion processes and are resistant to many chemicals.
Low weight – >synthetic materials are significantly lighter than many traditional materials such as metal or glass. The low weight directly reduces transportation and production costs, which is a key factor in competitiveness in many industrial sectors.
Don't wait!
Tailor the technology to your needs to reduce plastic production costs.
Low cost – >one of the most important factors contributing to the popularity of plastic is its low price. Plastic is an inexpensive material, both in terms of production and processing. This allows it to be widely used in many fields, from packaging to household tools and machine parts.
Versatility – >synthetic materials are incredibly versatile. They can be adapted to many applications, which is why they are found in products with various mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. From home appliances to vehicles, plastic is used in various contexts, fulfilling a range of functions.
Ease of processing -> Plastics are characterized by their ease of processing, allowing for the creation of products in various shapes and sizes.
Applications of Plastics
Plastics are used in many fields, from packaging to household goods, medicine, electronics, as well as the automotive and aerospace industries. Their versatility makes them indispensable in many aspects of our lives.
Plastics are also used in the heating industry, as described in a dedicated article.

Example plastic products
Examples of products from rotational molding include various toys, containers, and home and garden equipment components.
Injection molded products include bottles, toys, electronics components, as well as automotive parts like dashboards.
The extrusion process is used for producing pipes, profiles, foils, and structural components. Thermoformed products, on the other hand, include packaging, food trays, casings for medical products, and decorative elements.
Plastic materials are also used in the production of plastic bags and in bottle manufacturing.
The environmental aspect of plastics
Plastics are relatively difficult to decompose, posing an environmental problem. The term “plastic waste” is frequently mentioned in various media outlets.
Polymers of natural origin are not as environmentally concerning because they decompose relatively easily and naturally, whereas petroleum-based polymers pose a much greater challenge.
The fact is that conscious and responsible use of plastic can mitigate its negative impact on the natural environment.
One approach to responsible manufacturing is using a circular economy system in production. This means reusing materials or their leftovers that have been through the production process before. By collecting, storing, and then breaking down these materials, we get regrind, which is frequently and effectively used in various applications.
Another solution is the use of biodegradable plastics.
A universal principle is also to create long-lasting products that will be used for many years.
Plastics are a very diverse group of materials with many types that vary significantly in their properties and production methods.
Due to its unique properties, plastic finds a very wide range of applications and is very difficult to replace.
Nowadays, a lot is said about plastic (and rightly so!) in the context of ecology. It’s important to remember that a conscious approach through the use of regranulates and the production of long-lasting products means that the use of plastic does not have to negatively impact the natural environment.
Are you considering plastic production? Consult your project with us and learn the necessary knowledge to determine its feasibility.